PsoriasisIs a chronic disease that affects the skin, sometimes nails, joints and internal organs. It is manifested by itching and the appearance of pink-red rashes - papules, which can merge into larger plaques. These papules rise above the surface of the skin. They are covered with silvery scales that peel off easily when peeling.
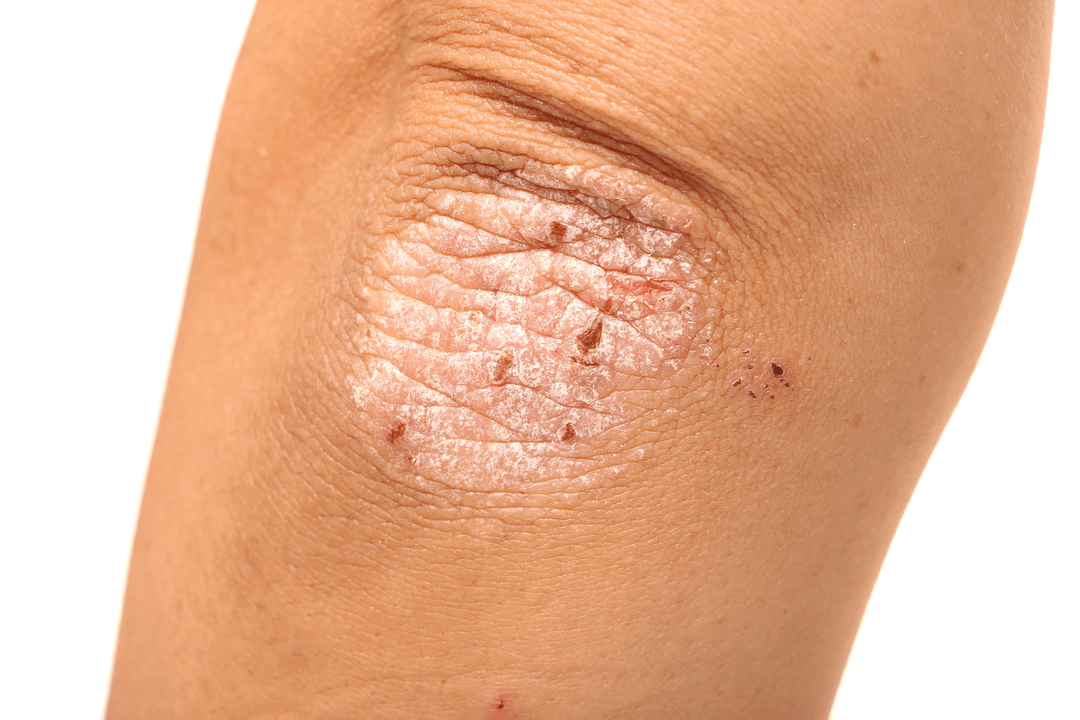
Quite often, the disease is combined with impotence, accelerated ejaculation and Reiter's syndrome. With extensive psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis can occur.
Risk factors
Causes of psoriasishave not yet been fully identified. Risk factors for the development of the disease include:
- microbial factor - various types of fungus, mycoplasma;
- neuropsychic trauma, stress;
- endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease;
- foci of chronic infection, especially streptococcal;
- immunodeficiency states;
- disorders of lipid and protein metabolism;
- injuries to the skin and joints.
Is psoriasis transmitted?
Psoriasis is not contagious. Many researchers pay attention to the familial nature of psoriasis and recognize its genetic nature. Moreover, it is not the disease itself that is inherited, but a predisposition to it.
If you find similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous to your health!
Psoriasis symptoms
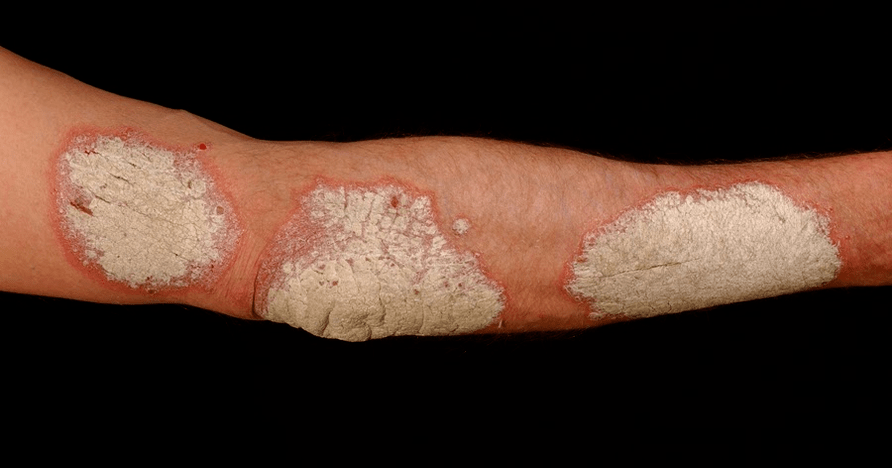
The first symptoms of psoriasis:rashes on the skin in the form of bright pink plaques with a scaly surface. Plaques are single, rise above the level of healthy skin, are located on the elbows and in the popliteal hollows.
More often, psoriatic plaques appear on the skin of the knees, elbows, chest, abdomen, back and scalp, but with the progression of the disease, they can appear in any other, most unexpected places of the integument.
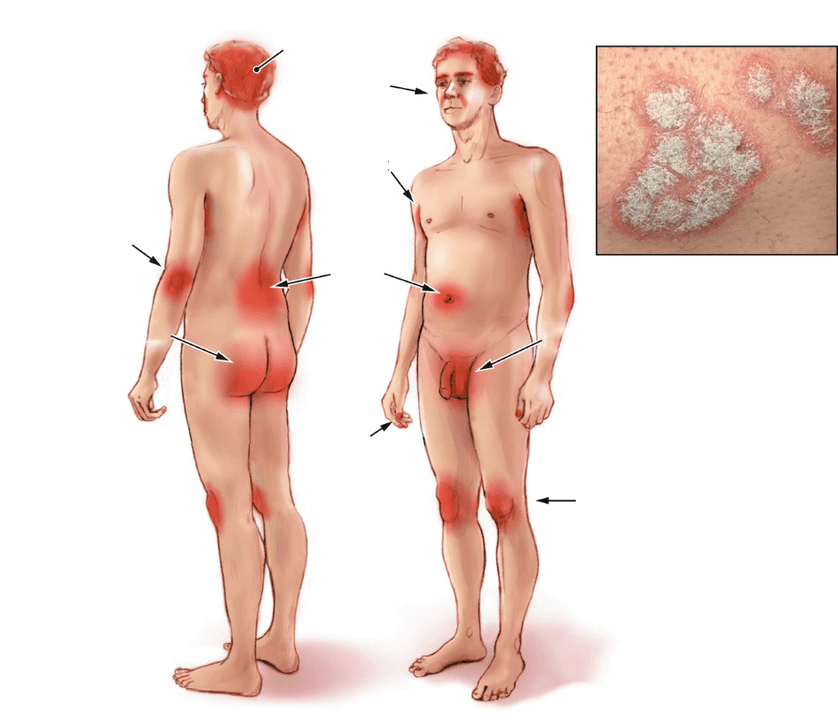
Initially, the papules are small - 3-5 mm, the color is bright pink. Gradually increasing in size, they become covered with silvery scales and merge into larger formations called plaques.
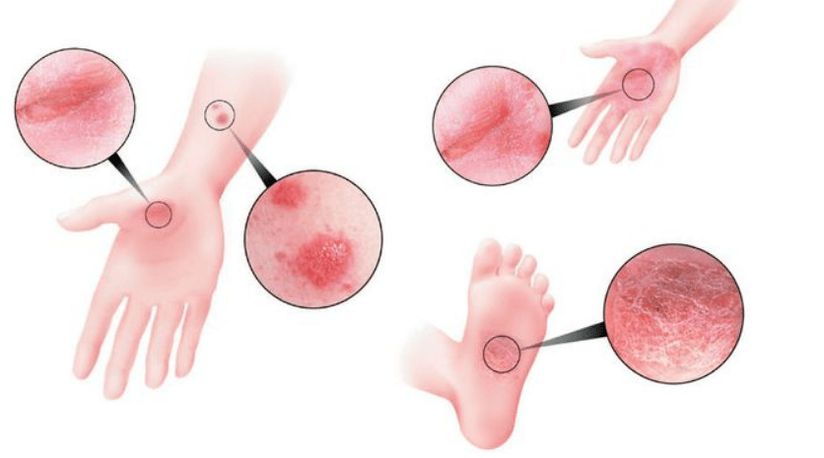
Fresh elements of papules, as a rule, are bright in color, up to red, "old" ones are more faded. At the initial stage of psoriasis, the edges of the papules do not peel off. They represent a hyperemic border -growth corolla. . .
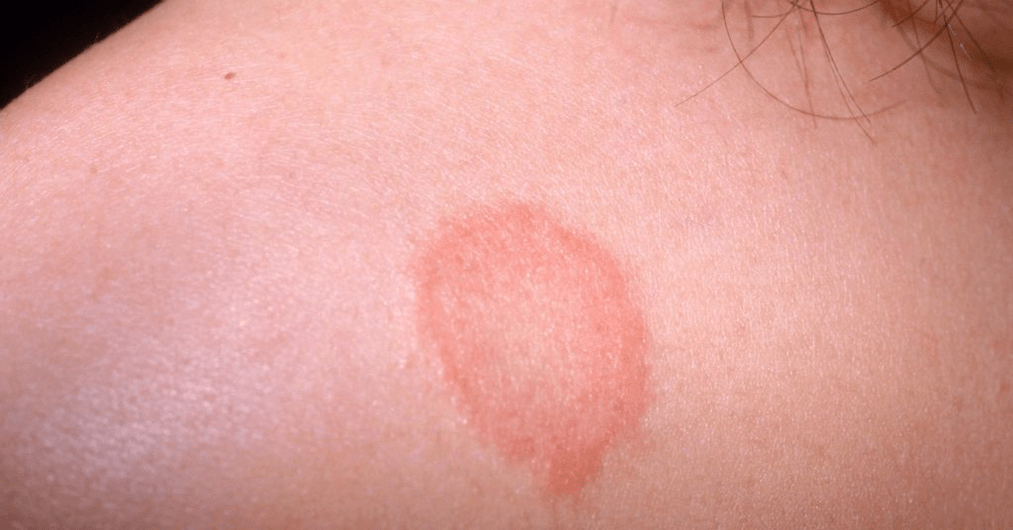
The hallmark of psoriasis is the Auspitz triad. This triad can be observed by scraping the surface of the papule with a sharp object. It includes three phenomena:
- stearin spot phenomenon- layering of a large number of silvery-white scales, which are easily separated when scraped;
- psoriatic film symptom- exudated surface, made with a prickly layer, which opens after peeling off the lower layers of the stratum corneum;
- blood dew phenomenon- exposure of superficial capillaries in the form of small blood spots after detachment of the psoriatic film.
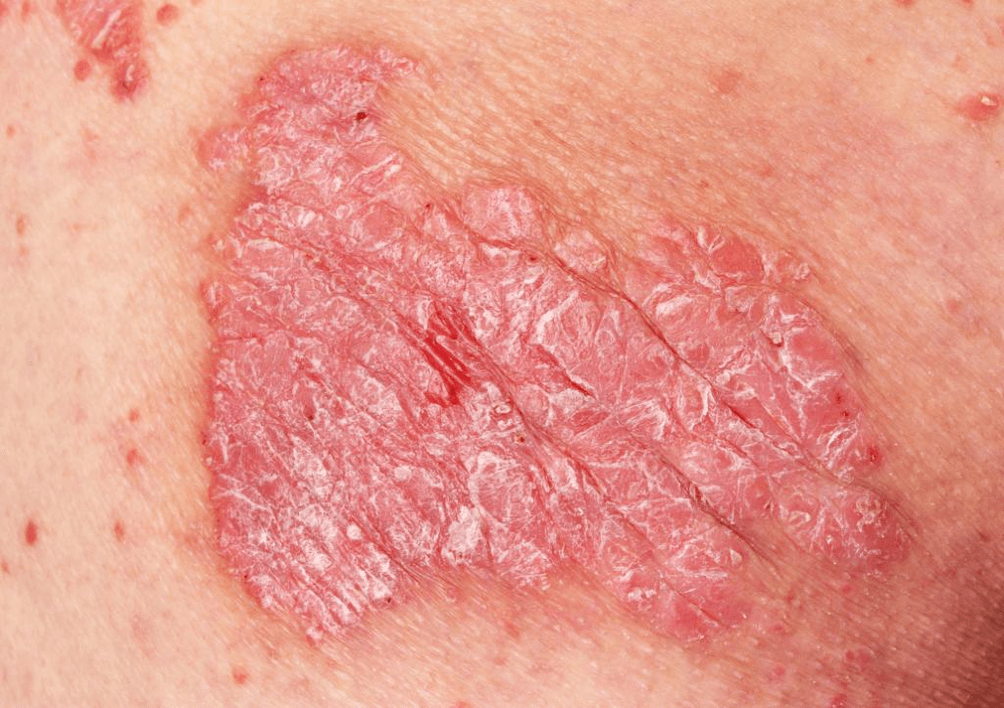
Signs of different types of psoriasis
Clinical types of psoriasis:
- Spotted psoriasis- represented by pale pink weakly infiltrated spots. It resembles toxidermia.
- Irritated psoriasis- occurs due to exposure to the skin of aggressive environmental factors (sunlight, cold, heat) and irritating drugs. The color of the plaque becomes more intense, it increases in size, rises more above the surface of the skin, a belt forms at the edges in the form of redness.
- Seborrheic psoriasis- often develops in patients with seborrhea. The clinical picture is very similar to seborrheic eczema.
- Exudative psoriasis- occurs quite often. It occurs due to the excessive secretion of an inflammatory fluid - exudate. It impregnates the accumulations of scales, turning them into scales-crusts.
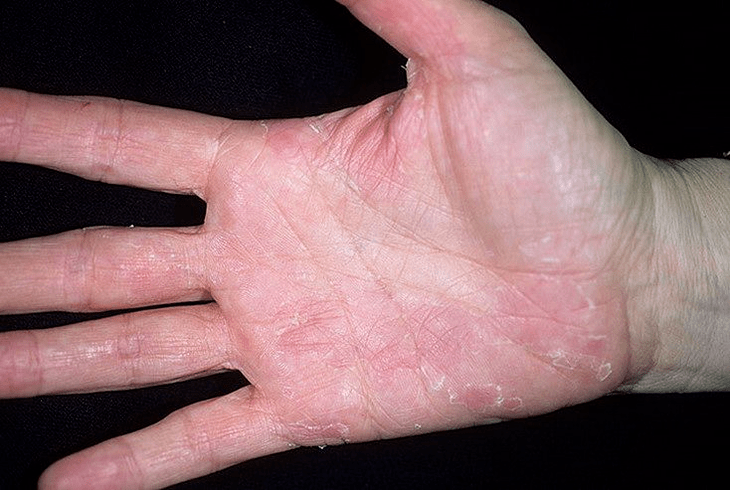
- Psoriasis of the palms and soles- represented by either common plaques and papules, or hyperkeratotic formations, similar to calluses and calluses.
- Follicular psoriasis- a rare form of the disease. The rash consists of white miliary nodules with a funnel-shaped depression in the center.
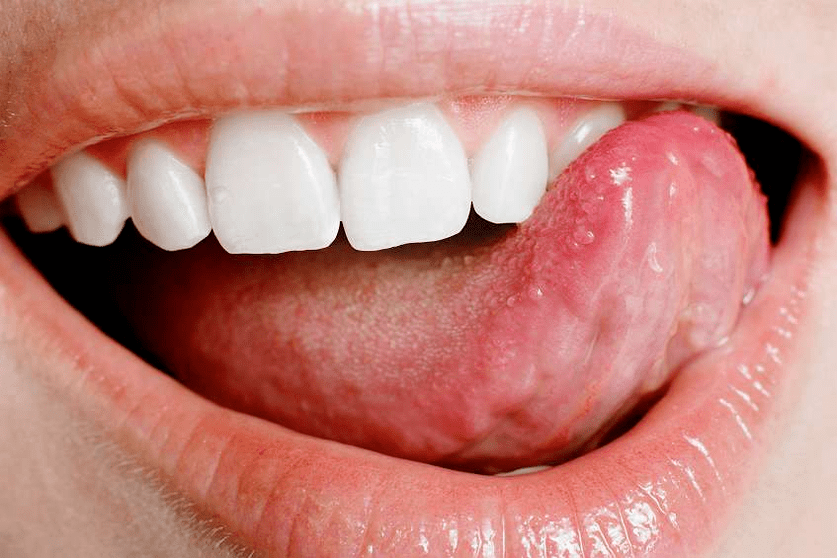
- Psoriasis of the mucous membranes- a rare form of the disease. It occurs on the mucous membrane of the mouth and bladder. It manifests itself in the form of areas of gray-white color with a red border.
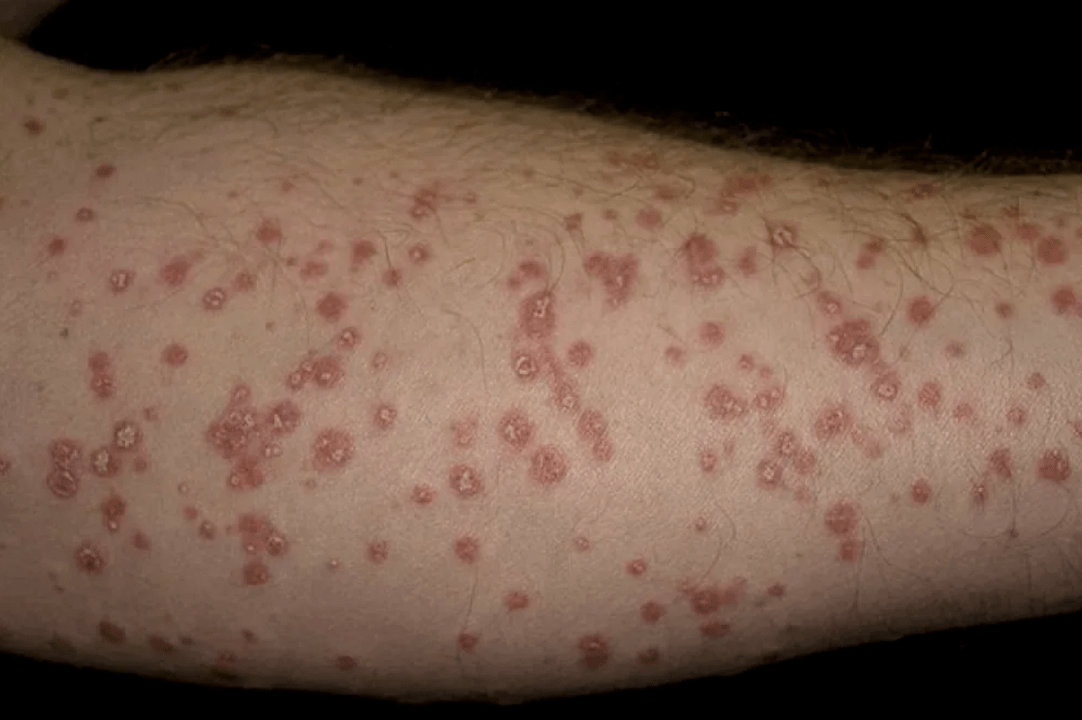
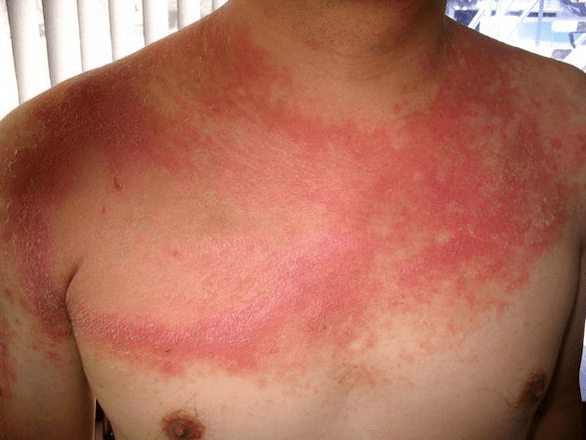
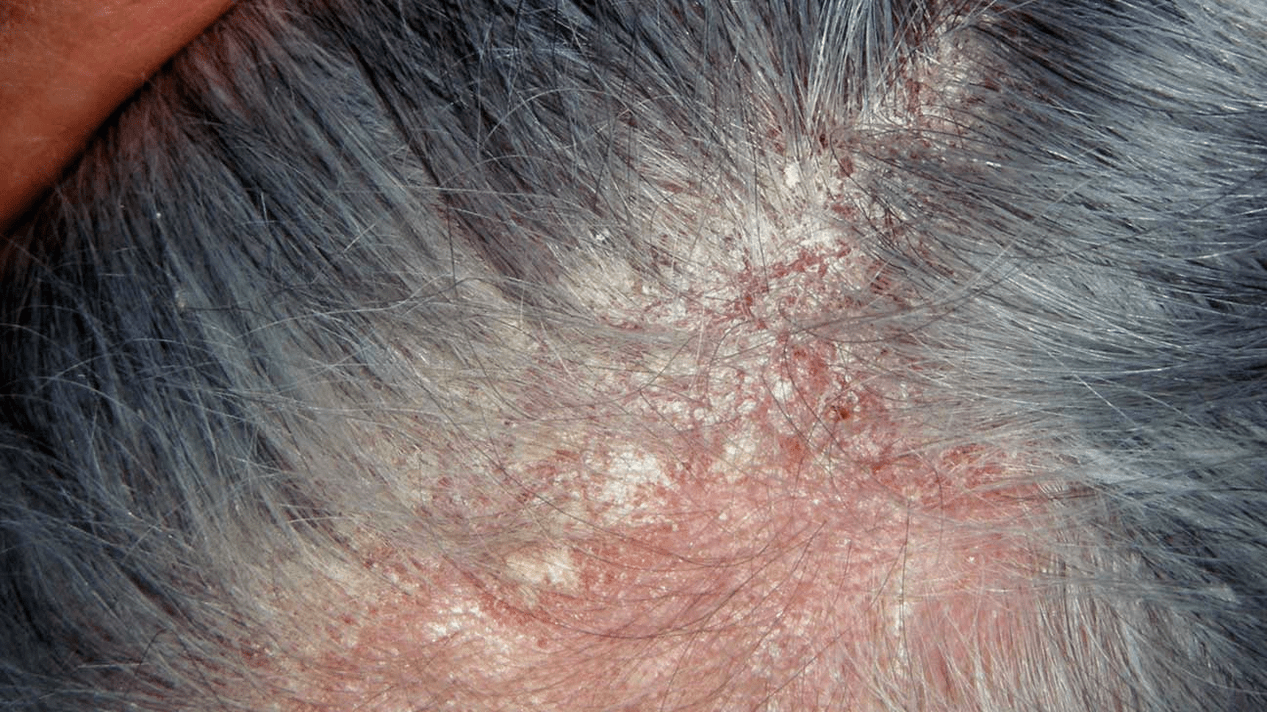
Frequency of psoriatic manifestations
Cyclic exacerbations are characteristic of psoriasis. Most often they occur in autumn and spring.
Pathogenesis of psoriasis
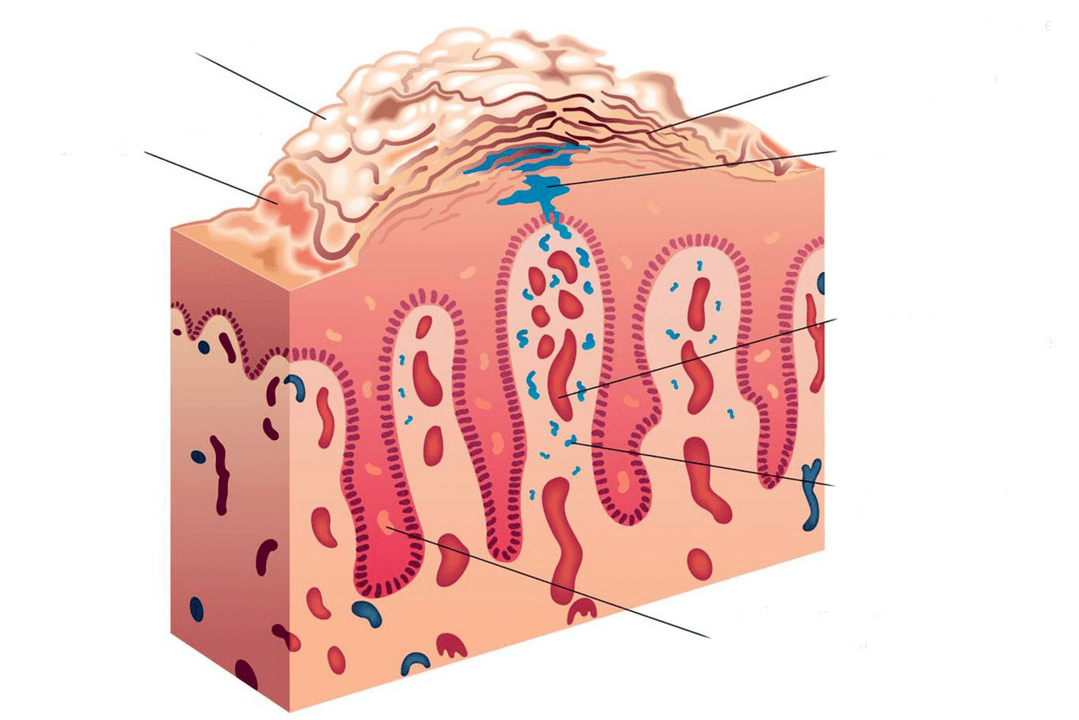
Dermatosis is an inflammatory process associated with the work of immune T cells. As a result of this inflammation, the proliferation of keratinocytes, the main cells of the epidermis, is accelerated.
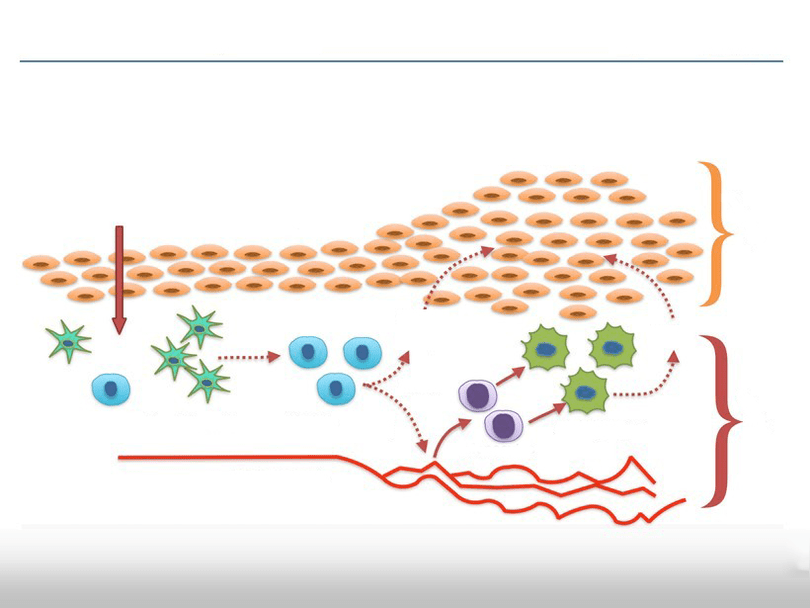
Psoriasis, a type of dermatosis, is a chronic inflammatory disease. It proceeds with the participation of microbial pathogens that can bind to the surface of the skin.
Everything that happens in the skin under the influence of the pathogen is a classic inflammatory reaction according to the principle of RTCDF:
- Rubor - redness;
- Tumor - tubercle, edema;
- Calor - fever, fever;
- Dolor - pain;
- Functia laesa - dysfunction.
Redness and thickening of the skin at the lesion sites, itching, increased keratinization followed by the formation of scales - all these are manifestations of the inflammatory process, a protective reaction of the body aimed at combating the microbial pathogen. Without timely outside help, the body is often defeated.
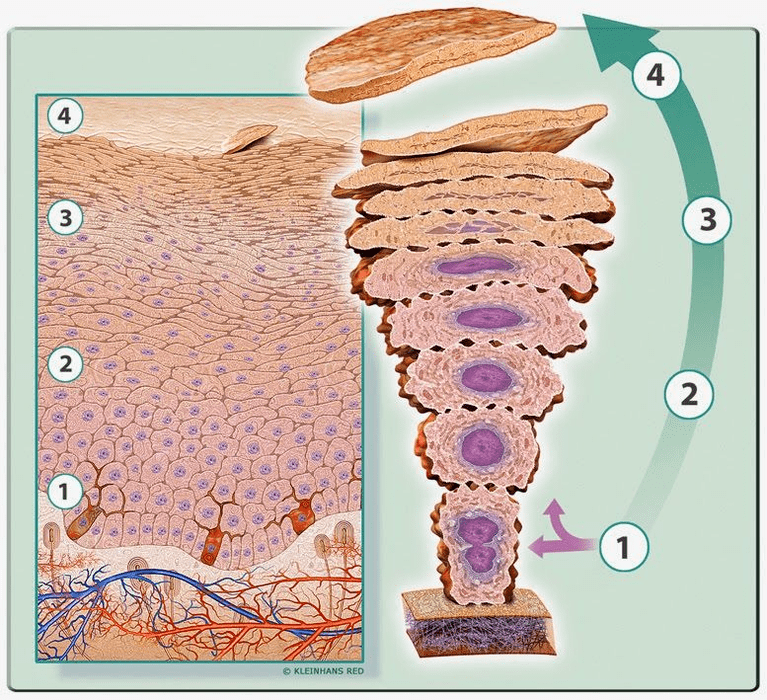
Some scientists adhere to the theory of a genetic predisposition to a violation of the process of cell division. With such a violation, there is an increased death and keratinization of cells with their subsequent growth and the appearance of a large number of incompletely keratinized epithelial cells. But this theory does not in the least contradict the above microbial.
Classification and stages of development of psoriasis
There is no generally accepted classification of psoriasis.
Traditionallythere are four types of the disease:
- vulgar psoriasis - seborrheic, follicular, warty, exudative, bullous, psoriasis of the palms and soles, psoriasis of the mucous membranes;
- pustular psoriasis;
- psoriatic erythroderma;
- psoriatic arthritis.
According to ICD-10, there are:
- L40. 0 Psoriasis vulgaris (coin and plaque psoriasis);
- L40. 1 Generalized pustular psoriasis (impetigo herpetiformis, Tsumbusch disease);
- L40. 2 Acrodermatitis persistent;
- L40. 3 Palmar and plantar pustulosis;
- L40. 4 Psoriasis teardrop;
- L40. 5 Arthropathic psoriasis;
- L40. 8 Other psoriasis;
- L40. 9 Psoriasis, unspecified
Complications of psoriasis
Without timely and competent treatment, psoriasis begins to negatively affect vital organs and systems: joints, heart, kidneys and nervous system. These conditions can lead to disability and even death.
What is psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is the most severe form of psoriasis, as it often causes disability.
Doctors face this complication most often. It occurs as a result of inflammatory changes in the joints.
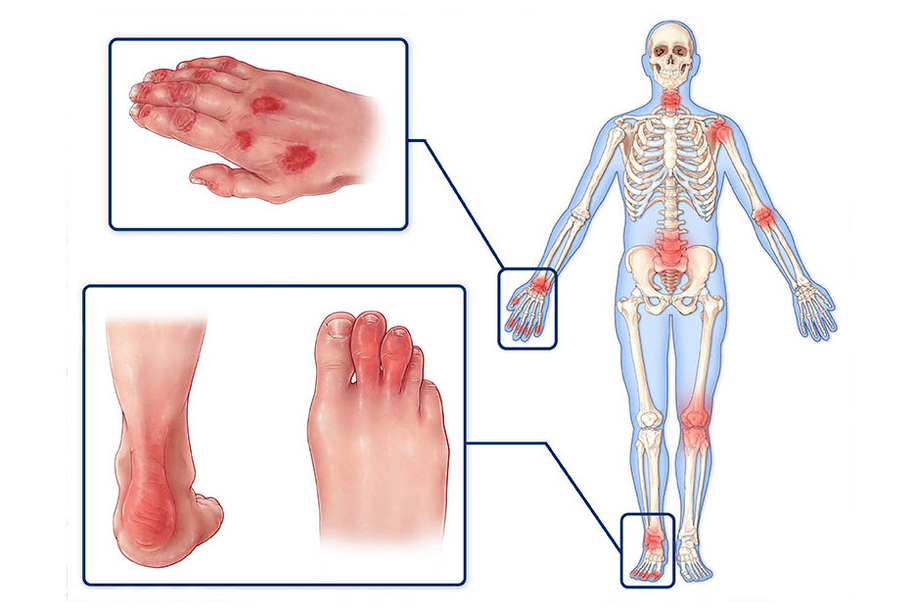
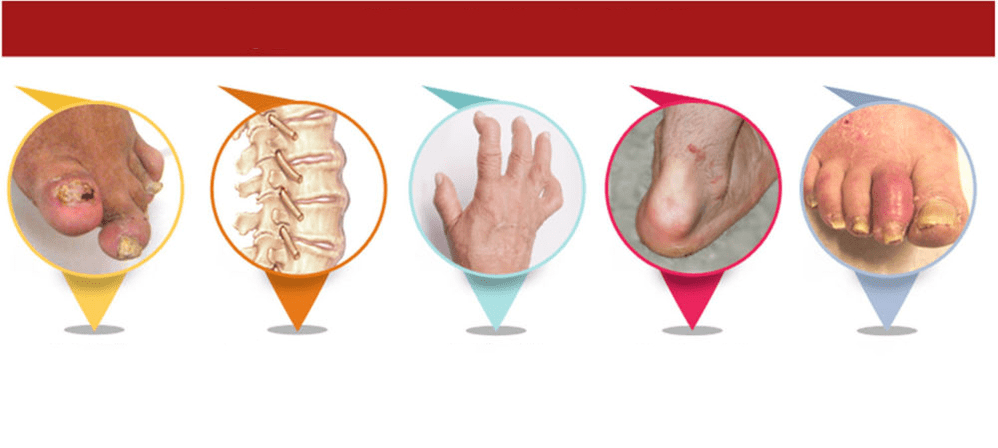
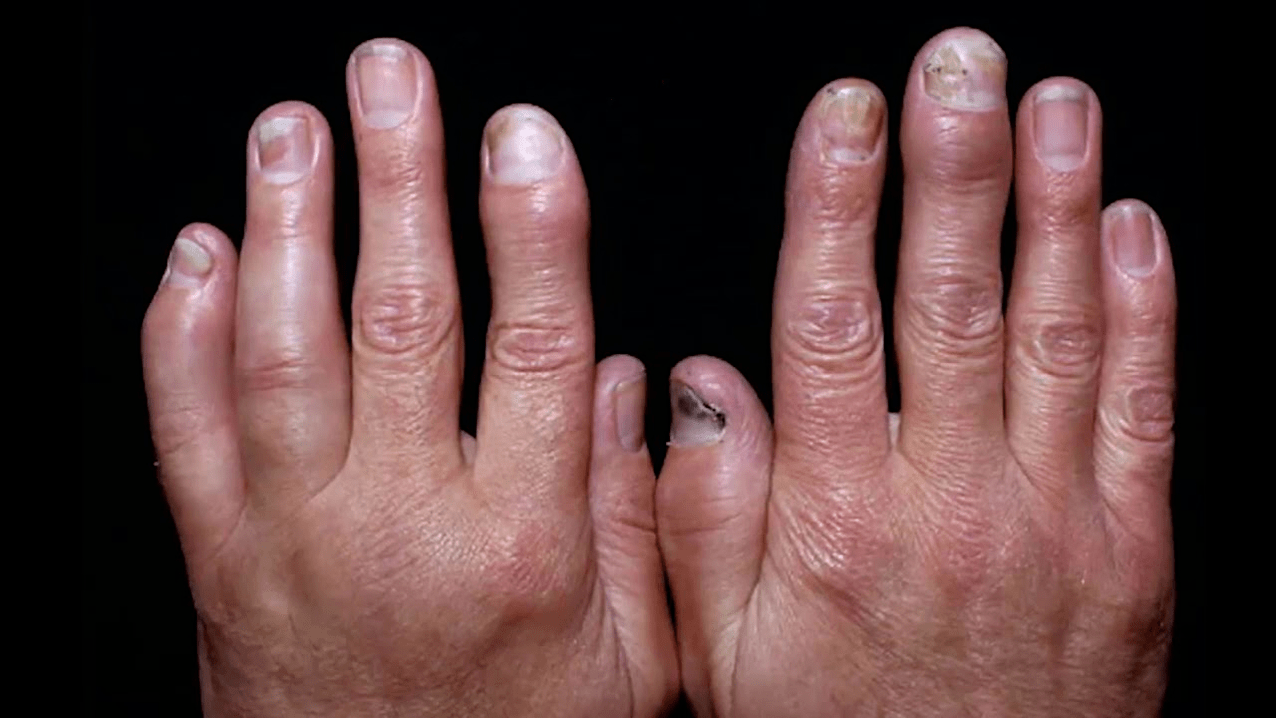
The joints of the hands, wrists, feet and knees are most affected. Over time, the disease can spread to the hip, shoulder and spinal joints. With further progression, muscles begin to ache near the affected joints. Patients complain of stiffness, especially in the morning. Their body temperature is often elevated throughout the day.
The clinical picture of psoriatic arthritis develops as usual arthritis: first, there is pain, then swelling, stiffness and limitation of mobility. A characteristic symptom of this complication is a sausage finger. It appears due to the defeat of all interphalangeal surfaces.
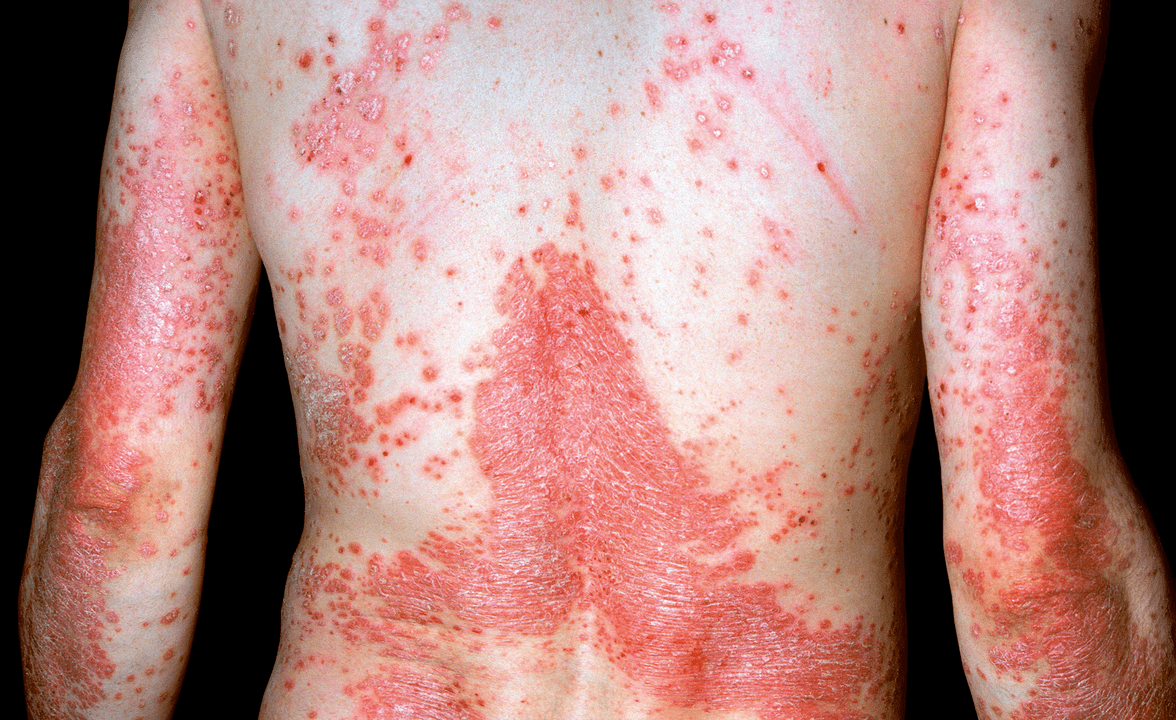
Other complications of psoriasis
Slightly less commonpsoriatic erythroderma. . .This condition occurs when the skin is completely affected. Patients are worried about itching and burning, profuse peeling of dead tissue, a strong reaction of the skin to a change in temperature.
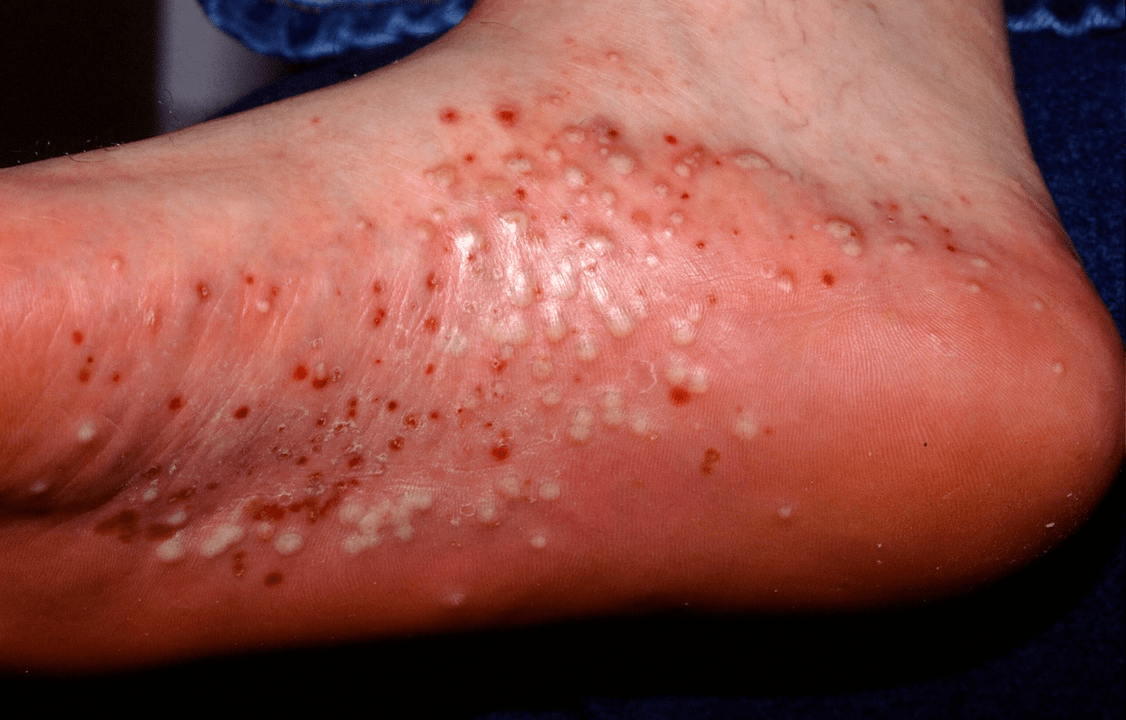
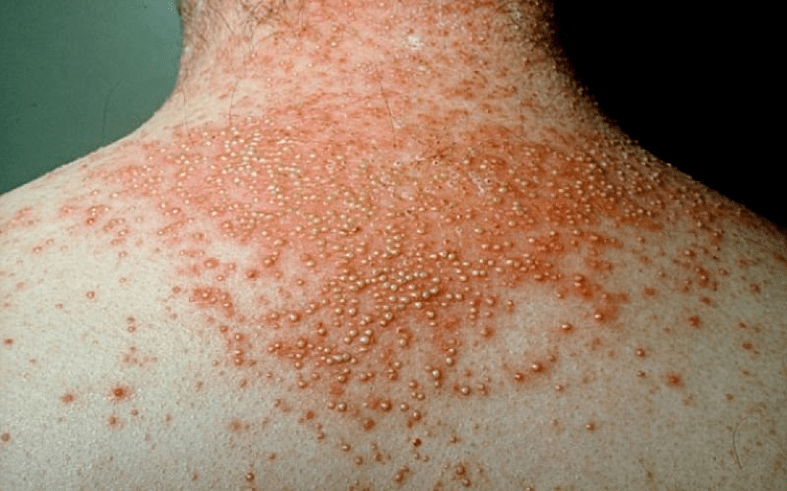
The next most frequent occurrence ispustular psoriasis. . .This complication is associated with the addition of a secondary infection - staphylococci and streptococci. Clinically, pustular psoriasis is accompanied by the appearance of pustules - pustules the size of a buckwheat grain. The pustules appear in different places. They rise above the surface of the skin, are characterized by rapid growth and a tendency to merge. The existing symptoms are joined by high fever and signs of serious intoxication.
Lesions of internal organswith psoriasis are now extremely rare. As a rule, people who lead an asocial lifestyle are susceptible to them. The genitourinary system is more often affected: the kidneys, the mucous membrane of the bladder and urethra. This leads to the development of pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis and urethritis.
On the part of the heart, psoriasis can cause damage to the mitral valves, inflammation of the heart muscle and the outer lining of the heart - myocarditis and pericarditis. With damage to the nervous system, patients complain of a creeping sensation, increased irritability or depression, constant fatigue, drowsiness and apathy.
Diagnostics of the psoriasis
When to see a doctor
It is necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of psoriasis: the appearance on the skin of bright pink plaques with a flaky surface.
Preparing to visit a doctor
Three days before visiting a doctor, you should stop applying medicinal ointments to the skin. No other special training is required.
Psoriasis is such a recognizable disease that it will not be difficult to diagnose it based on external signs. Often, a diagnosis can be made to patients, as they say, "out of the box. "If necessary, the doctor scrapes the surface of the skin to detect the Auspitz triad.
OV Terletskiy, Candidate of Medical Sciences, together with co-authors, proposed a diagnostic scheme developed on the basis of data from the American Rheumatological Association. It includes the following examinations:
- complete blood count (with platelets);
- general urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- acute phase reactions of the body - C-reactive protein and rheumatoid factor;
- immunoglobulins - IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE)
- reaction of complement binding with gonococcal and chlamydial antigen;
- the Wright and Heddelson reactions;
- coagulogram - assessment of blood coagulation;
- blood test for borreliosis and toxoplasmosis (according to indications);
- blood test for HLA.
However, there are many diseases under the guise of psoriasis. In this regard, it becomes necessary to conductdifferential diagnosis, in particular between papular syphilis, Reiter's syndrome, neurodermatitis, lichen rosacea, systemic lupus erythematosus and seborrheic eczema. For this purpose, use:
- biopsy - pinching off a piece of skin with subsequent histological examination;
- laboratory diagnostics - often used to distinguish psoriasis from papular syphilis;
- blood tests for other hidden infections for a better selection of antibiotics.
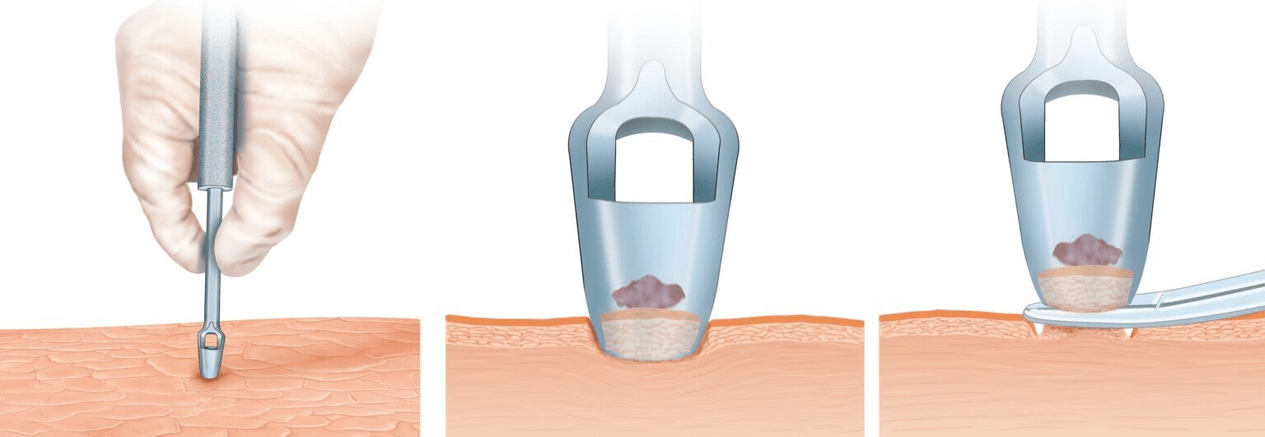
Instrumental diagnostic methodsmainly used for complicated forms of psoriasis associated with damage to the joints and internal organs. These include: X-rays of the joints, ultrasound of the heart, kidneys and bladder.
Psoriasis treatment
Is there an effective treatment for psoriasis
Despite the fact that psoriasis is a persistently recurrent disease, it can be completely eliminated provided that you consult a dermatologist in a timely manner, who can identify the true causes of psoriasis. Over the past decade, many drugs of systemic and local action have appeared, aimed at eliminating the cause and suppressing the mechanism of the development of the disease. Drugs that interact with each other using chemical signals (cytokines) have proven themselves very well. They eliminate the increased proliferation of skin creatinocytes.
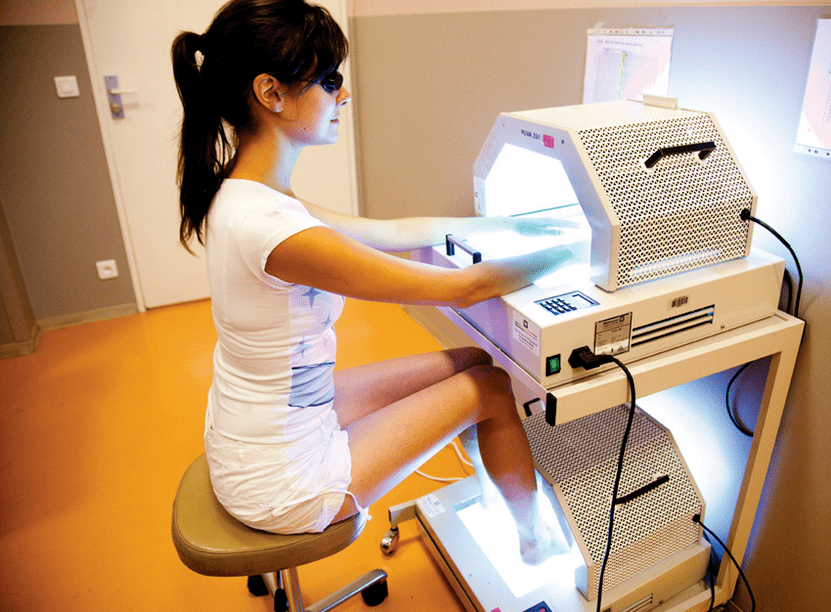
Phototherapy
In 1994, the team of the Department of Dermatovenereology of MAPO SPb introduced a method of treating psoriasis usingUFO blood- photomodification of blood with ultraviolet light.
The ability of sunlight to have a beneficial effect on the skin for numerous diseases, including psoriasis, has been known since time immemorial. At the beginning of the twentieth century, a group of German scientists suggested that since ultraviolet light has a healing effect on exposed skin, this effect is likely to occur when ultraviolet radiation is applied to the blood. After all, this is also a kind of fabric. This assumption was confirmed by the first session of UV exposure on blood, which was held in Germany in 1924.
The therapeutic effect of ultraviolet rays on the blood is associated with deep structural changes at the molecular-atomic level, which are captured by immunocompetent organs - the liver, spleen, bone marrow and lymphoid tissue. These changes are regarded by the organs as an alarm signal, and therefore they produce tens of times more immune complexes. In this case, ultraviolet light is a kind of "whip" that forces the body to dramatically increase its defenses to fight the disease.

Also worth noting is the PT effect -unlining ultraviolet therapy. . . This method of treatment is important, given the chronic nature of psoriasis, associated with numerous complications of internal organs caused by a variety of microbial pathogens. The longer the microbes are in the body, the wider their habitat becomes. These microscopic creatures capture more and more anatomical areas through the blood and lymph flow. Once in the tissues, they strive to penetrate as deeply as possible into the intercellular spaces. There they form microcolonies, protected by the remnants of dead, destroyed cells and a leukocyte shaft. Due to this, microorganisms can be out of the reach of antibiotics for years. They easily compensate for the lack of nutrients by entering a state of suspended animation - something between life and death.
The ability of ultraviolet rays helps to destroy microbial "shelters". They create favorable conditions for the penetration of antibiotics and other drugs that affect the cause of psoriasis.
Cutaneous application of ultraviolet radiation is also relevant. The most famous treatment method using this principle isPUVA therapy. . . Although it is less effective than blood ultraviolet irradiation. The therapeutic effect does not last long, a relapse may occur two weeks after the end of treatment.
Drug treatment
From medications, the following have worked well:
- derivatives of vitamin A, which reduce the rate of maturation of keratinocytes and normalize cell differentiation;
- immunosuppressants that reduce the activity of T-lymphocytes, which contribute to increased division of epidermal cells;
- drugs for the treatment of malignant tumors that inhibit the reproduction and growth of atypical skin cells.
What ointments and creams are effective in treating psoriasis
Ointments and creams with anti-inflammatory components will help to alleviate the patient's condition.
How to treat scalp psoriasis
Ointments are not effective in treating scalp psoriasis. In addition to medication and ultraviolet treatment, a special shampoo can be used.
How to treat psoriasis on elbows and arms
Psoriasis on the elbows and arms is treated with the same methods as for the rest of the body. The peculiarity of the course of psoriasis in this area is that the skin of the hands is subject to physical, mechanical and chemical influences, which is considered an aggravating factor in the course of the disease.
Is monoclonal antibody treatment for psoriasis effective?
Monoclonal antibody therapy for psoriasis is very effective. Monoclonal antibody drugs are lab-produced antibodies similar to those produced by human immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies selectively target targets responsible for the development of the disease.
How to recognize and treat psoriasis in children
In children, psoriasis often proceeds more violently and is disguised as other diseases (eczema, erysipelas, herpes), which complicates the diagnosis. The methods of therapy are similar to those for adults: phototherapy, medication and topical treatment.
What baths to take with psoriasis
Aloe baths can help reduce inflammation and itching.
How to treat psoriasis according to Pegano
The Pegano method for treating psoriasis involves bowel cleansing, diet and herbal teas. The effectiveness of this method has not been proven by clinical studies.
Role of nutrition in treatment
Nutrition greatly affects the course of psoriasis. When treating, it is necessary to exclude alcohol, salty, spicy, pickled, nuts, citrus fruits, honey, chocolate and smoked meats.
In which sanatoriums is rest indicated for the treatment of psoriasis
For psoriasis, spa treatment is preferable to take place on the sea in a region with a warm, dry climate and a lot of sunny days. The most suitable for this are the resorts of the Crimea.
Folk ways
Some folk remedies can help reduce itching and flaking of the skin in patients with mild to moderate psoriasis. These methods include:
- cream with aloe extract;
- fish oil applied to the skin with a coated bandage for six hours a day for four weeks;
- cream with oregon grape extract.
Forecast. Prevention
Psoriasis is not a sentence. If the patient has timely asked for qualified help from a specialist who can establish the real causes of the disease and prescribe effective treatment, then the disease will be defeated.
The simple form of psoriasis is manifested only by a skin defect. Therefore, the patient does not need special conditions for work. The exception is work at a chemical plant: in this case, staying at the workplace will have to be excluded.
It is worth remembering that psoriasis can cause complications. Most often, psoriatic arthritis develops. Its severe forms can limit the performance of duties at work, and in the future lead to complete disability.
Prevention of psoriasis is an integral part of therapeutic measures to eliminate one of the most serious skin diseases. After recovery, the patient needs to completely revise his lifestyle, eliminate bad habits, pay attention to the treatment of chronic diseases of other organs, adjust nutrition, include outdoor walks and sports in the daily routine.
Do they take with psoriasis in the army?
Severe forms of psoriasis are sufficient grounds for declaring a conscript unfit for military service, light forms - of limited suitability.























